Page 37 - EQTips_Eng
P. 37
IITK-BMTPC Earthquake Tip 18
How do Beams in RC Buildings resist Earthquakes? page 2
bars are (a) made away from the face of the column,
Bottom steel at supports At least 2 bars should go and (b) not made at locations where they are likely to
at least half of that at top
full length of beam stretch by large amounts and yield (e.g., bottom bars at
mid-length of the beam). Moreover, at the locations of
laps, vertical stirrups should be provided at a closer
spacing (Figure 6).
Beam
Total amount of steel Spacing of stirrups Spacing of stirrups
as calculated
as calculated
Column from calculation Column (but not more than d/4 (but not more than d/4
and 8 times beam bar and 8 times beam bar
Figure 3: Location and amount of longitudinal diameter) Spacing of stirrups diameter)
steel bars in beams – these resist tension due to as per calculations
(but not more than
flexure. 2d d/2) 2d
Stirrups in RC beams help in three ways, namely d
(i) they carry the vertical shear force and thereby resist
diagonal shear cracks (Figure 2b), (ii) they protect the 2d Beam 2d
concrete from bulging outwards due to flexure, and Column Column
(iii) they prevent the buckling of the compressed
longitudinal bars due to flexure. In moderate to severe Figure 5: Location and amount of vertical stirrups
seismic zones, the Indian Standard IS13920-1993 in beams – IS:13920-1993 limit on maximum
prescribes the following requirements related to spacing ensures good earthquake behaviour.
stirrups in reinforced concrete beams:
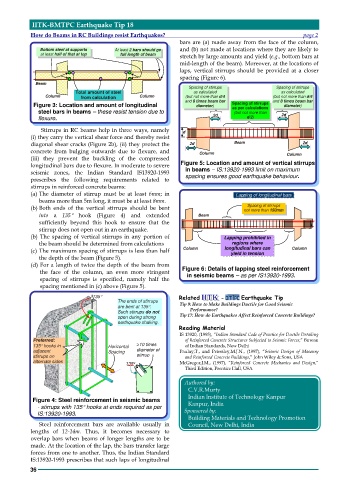
(a) The diameter of stirrup must be at least 6mm; in Lapping of longitudinal bars
beams more than 5m long, it must be at least 8mm.
Spacing of stirrups
(b) Both ends of the vertical stirrups should be bent not more than 150mm
into a 135° hook (Figure 4) and extended Beam
sufficiently beyond this hook to ensure that the
stirrup does not open out in an earthquake.
(b) The spacing of vertical stirrups in any portion of Lapping prohibited in
the beam should be determined from calculations regions where
(c) The maximum spacing of stirrups is less than half Column longitudinal bars can Column
yield in tension
the depth of the beam (Figure 5).
(d) For a length of twice the depth of the beam from
the face of the column, an even more stringent Figure 6: Details of lapping steel reinforcement
spacing of stirrups is specified, namely half the in seismic beams – as per IS13920-1993.
spacing mentioned in (c) above (Figure 5).
135°
The ends of stirrups Related - Earthquake Tip
are bent at 135°. Tip 9: How to Make Buildings Ductile for Good Seismic
Performance?
Such stirrups do not Tip 17: How do Earthquakes Affect Reinforced Concrete Buildings?
open during strong
earthquake shaking.
Reading Material
IS 13920, (1993), “Indian Standard Code of Practice for Ductile Detailing
Preferred: of Reinforced Concrete Structures Subjected to Seismic Forces,” Bureau
135° hooks in Horizontal ≥10 times of Indian Standards, New Delhi
adjacent Spacing diameter of Paulay,T., and Priestley,M.J.N., (1997), “Seismic Design of Masonry
stirrups on stirrup and Reinforced Concrete Buildings,” John Wiley & Sons, USA
alternate sides 135º McGregor,J.M., (1997), “Reinforced Concrete Mechanics and Design,“
Third Edition, Prentice Hall, USA
Authored by:
C.V.R.Murty
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
Figure 4: Steel reinforcement in seismic beams
- stirrups with 135° hooks at ends required as per Kanpur, India
IS:13920-1993. Sponsored by:
Building Materials and Technology Promotion
Steel reinforcement bars are available usually in Council, New Delhi, India
lengths of 12-14m. Thus, it becomes necessary to
overlap bars when beams of longer lengths are to be
made. At the location of the lap, the bars transfer large
forces from one to another. Thus, the Indian Standard
IS:13920-1993 prescribes that such laps of longitudinal
36