Page 38 - EQTips_Eng
P. 38
Learning
19 Earthquake Design
Earthquake Tip and
Construction
How do Columns in RC Buildings resist Earthquakes?
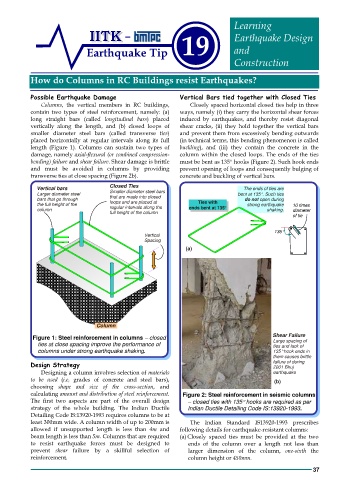
Possible Earthquake Damage Vertical Bars tied together with Closed Ties
Columns, the vertical members in RC buildings, Closely spaced horizontal closed ties help in three
contain two types of steel reinforcement, namely: (a) ways, namely (i) they carry the horizontal shear forces
long straight bars (called longitudinal bars) placed induced by earthquakes, and thereby resist diagonal
vertically along the length, and (b) closed loops of shear cracks, (ii) they hold together the vertical bars
smaller diameter steel bars (called transverse ties) and prevent them from excessively bending outwards
placed horizontally at regular intervals along its full (in technical terms, this bending phenomenon is called
length (Figure 1). Columns can sustain two types of buckling), and (iii) they contain the concrete in the
damage, namely axial-flexural (or combined compression- column within the closed loops. The ends of the ties
bending) failure and shear failure. Shear damage is brittle must be bent as 135° hooks (Figure 2). Such hook ends
and must be avoided in columns by providing prevent opening of loops and consequently bulging of
transverse ties at close spacing (Figure 2b). concrete and buckling of vertical bars.
Vertical bars Closed Ties The ends of ties are
Larger diameter steel Smaller diameter steel bars bent at 135°. Such ties
bars that go through that are made into closed do not open during
the full height of the loops and are placed at Ties with strong earthquake 10 times
column regular intervals along the ends bent at 135° shaking. diameter
full height of the column
of tie
Vertical 135°
Spacing
(a)
Column
ties at close spacing improve the performance of Shear Failure
Figure 1: Steel reinforcement in columns –closed
Large spacing of
columns under strong earthquake shaking. ties and lack of
135° hook ends in
them causes brittle
Design Strategy failure of during
2001 Bhuj
Designing a column involves selection of materials earthquake
to be used (i.e, grades of concrete and steel bars), (b)
choosing shape and size of the cross-section, and
calculating amount and distribution of steel reinforcement. Figure 2: Steel reinforcement in seismic columns
The first two aspects are part of the overall design – closed ties with 135° hooks are required as per
strategy of the whole building. The Indian Ductile Indian Ductile Detailing Code IS:13920-1993.
Detailing Code IS:13920-1993 requires columns to be at
least 300mm wide. A column width of up to 200mm is The Indian Standard IS13920-1993 prescribes
allowed if unsupported length is less than 4m and following details for earthquake-resistant columns:
beam length is less than 5m. Columns that are required (a) Closely spaced ties must be provided at the two
to resist earthquake forces must be designed to ends of the column over a length not less than
prevent shear failure by a skillful selection of larger dimension of the column, one-sixth the
reinforcement. column height or 450mm.
37