Page 22 - EQTips_Eng
P. 22
Learning
11 Earthquake Design
Earthquake Tip and
Construction
What are the Indian Seismic Codes?
Importance of Seismic Design Codes IS 13935, 1993, Indian Standard Guidelines for Repair and
Ground vibrations during earthquakes cause Seismic Strengthening of Buildings
forces and deformations in structures. Structures need The regulations in these standards do not ensure
to be designed to withstand such forces and that structures suffer no damage during earthquake of
deformations. Seismic codes help to improve the all magnitudes. But, to the extent possible, they ensure
behaviour of structures so that they may withstand the that structures are able to respond to earthquake
earthquake effects without significant loss of life and shakings of moderate intensities without structural
property. Countries around the world have damage and of heavy intensities without total collapse.
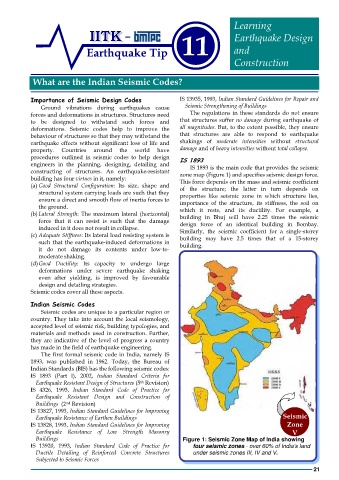
procedures outlined in seismic codes to help design IS 1893
engineers in the planning, designing, detailing and IS 1893 is the main code that provides the seismic
constructing of structures. An earthquake-resistant zone map (Figure 1) and specifies seismic design force.
building has four virtues in it, namely: This force depends on the mass and seismic coefficient
(a) Good Structural Configuration: Its size, shape and of the structure; the latter in turn depends on
structural system carrying loads are such that they properties like seismic zone in which structure lies,
ensure a direct and smooth flow of inertia forces to importance of the structure, its stiffness, the soil on
the ground.
(b) Lateral Strength: The maximum lateral (horizontal) which it rests, and its ductility. For example, a
building in Bhuj will have 2.25 times the seismic
force that it can resist is such that the damage design force of an identical building in Bombay.
induced in it does not result in collapse. Similarly, the seismic coefficient for a single-storey
(c) Adequate Stiffness: Its lateral load resisting system is building may have 2.5 times that of a 15-storey
such that the earthquake-induced deformations in building.
it do not damage its contents under low-to-
moderate shaking.
(d) Good Ductility: Its capacity to undergo large
deformations under severe earthquake shaking
even after yielding, is improved by favourable
design and detailing strategies.
Seismic codes cover all these aspects.
Indian Seismic Codes
Seismic codes are unique to a particular region or
country. They take into account the local seismology,
accepted level of seismic risk, building typologies, and
materials and methods used in construction. Further,
they are indicative of the level of progress a country
has made in the field of earthquake engineering.
The first formal seismic code in India, namely IS
1893, was published in 1962. Today, the Bureau of
Indian Standards (BIS) has the following seismic codes:
IS 1893 (Part I), 2002, Indian Standard Criteria for
Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures (5 Revision)
th
IS 4326, 1993, Indian Standard Code of Practice for
Earthquake Resistant Design and Construction of
Buildings (2 Revision)
nd
IS 13827, 1993, Indian Standard Guidelines for Improving
Earthquake Resistance of Earthen Buildings Seismic
IS 13828, 1993, Indian Standard Guidelines for Improving Zone
Earthquake Resistance of Low Strength Masonry V
Buildings Figure 1: Seismic Zone Map of India showing
IS 13920, 1993, Indian Standard Code of Practice for four seismic zones - over 60% of India’s land
Ductile Detailing of Reinforced Concrete Structures under seismic zones III, IV and V.
Subjected to Seismic Forces
21