Page 27 - EQTips_Eng
P. 27
IITK-BMTPC Earthquake Tip 13
Why should Masonry Buildings have simple Structural Configuration? page 2
Large window Tall
opening
reduces the slender
wall strength wall
in its strong
direction
Inertia force of
Damage roof mass
Damage
Diagonal
bracing
Door opening close to wall corner effect
weakens the connection between walls Damage
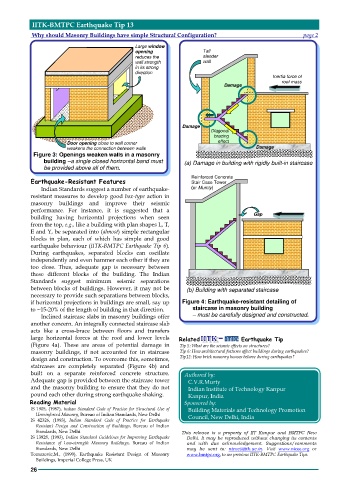
Figure 3: Openings weaken walls in a masonry
building –a single closed horizontal band must (a) Damage in building with rigidly built-in staircase
be provided above all of them.
Reinforced Concrete
Earthquake-Resistant Features Stair Case Tower
Indian Standards suggest a number of earthquake- (or Mumty)
resistant measures to develop good box-type action in
masonry buildings and improve their seismic
performance. For instance, it is suggested that a Gap
building having horizontal projections when seen
from the top, e.g., like a building with plan shapes L, T,
E and Y, be separated into (almost) simple rectangular
blocks in plan, each of which has simple and good
earthquake behaviour (IITK-BMTPC Earthquake Tip 6).
During earthquakes, separated blocks can oscillate
independently and even hammer each other if they are
too close. Thus, adequate gap is necessary between
these different blocks of the building. The Indian
Standards suggest minimum seismic separations
between blocks of buildings. However, it may not be (b) Building with separated staircase
necessary to provide such separations between blocks,
if horizontal projections in buildings are small, say up Figure 4: Earthquake-resistant detailing of
to ~15-20% of the length of building in that direction. staircase in masonry building
Inclined staircase slabs in masonry buildings offer – must be carefully designed and constructed.
another concern. An integrally connected staircase slab
acts like a cross-brace between floors and transfers
large horizontal forces at the roof and lower levels Related Earthquake Tip
(Figure 4a). These are areas of potential damage in Tip 5: What are the seismic effects on structures?
masonry buildings, if not accounted for in staircase Tip 6: How architectural features affect buildings during earthquakes?
design and construction. To overcome this, sometimes, Tip12: How brick masonry houses behave during earthquakes?
staircases are completely separated (Figure 4b) and
built on a separate reinforced concrete structure. Authored by:
Adequate gap is provided between the staircase tower C.V.R.Murty
and the masonry building to ensure that they do not Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
pound each other during strong earthquake shaking. Kanpur, India
Reading Material Sponsored by:
IS 1905, (1987), Indian Standard Code of Practice for Structural Use of Building Materials and Technology Promotion
Unreinforced Masonry, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi Council, New Delhi, India
IS 42326, (1993), Indian Standard Code of Practice for Earthquake
Resistant Design and Construction of Buildings, Bureau of Indian
Standards, New Delhi This release is a property of IIT Kanpur and BMTPC New
IS 13828, (1993), Indian Standard Guidelines for Improving Earthquake Delhi. It may be reproduced without changing its contents
Resistance of Low-strength Masonry Buildings, Bureau of Indian and with due acknowledgement. Suggestions/comments
Standards, New Delhi may be sent to: nicee@iitk.ac.in. Visit www.nicee.org or
Tomazevic,M., (1999), Earthquake Resistant Design of Masonry www.bmtpc.org, to see previous IITK-BMTPC Earthquake Tips.
Buildings, Imperial College Press, UK
26