Page 30 - EQTips_Eng
P. 30
Learning
15 Earthquake Design
Earthquake Tip and
Construction
Why is Vertical Reinforcement required in Masonry Buildings?
Response of Masonry Walls
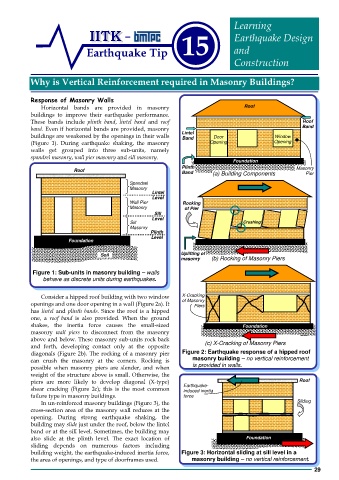
Horizontal bands are provided in masonry Roof
buildings to improve their earthquake performance.
These bands include plinth band, lintel band and roof Roof
band. Even if horizontal bands are provided, masonry Band
Lintel
buildings are weakened by the openings in their walls Band Door Window
(Figure 1). During earthquake shaking, the masonry Opening Opening
walls get grouped into three sub-units, namely
spandrel masonry, wall pier masonry and sill masonry.
Foundation
Plinth
Roof Soil Masonry
Band
(a) Building Components Pier
Spandrel
Masonry
Lintel
Level
Wall Pier Rocking
Masonry of Pier
Sill
Level
Sill Crushing
Masonry Plinth
Foundation Level
Soil
Uplifting of
masonry
(b) Rocking of Masonry Piers
Figure 1: Sub-units in masonry building – walls
behave as discrete units during earthquakes.
Consider a hipped roof building with two window X-Cracking
openings and one door opening in a wall (Figure 2a). It of Masonry
Piers
has lintel and plinth bands. Since the roof is a hipped
one, a roof band is also provided. When the ground
shakes, the inertia force causes the small-sized Foundation
masonry wall piers to disconnect from the masonry Soil
above and below. These masonry sub-units rock back
and forth, developing contact only at the opposite (c) X-Cracking of Masonry Piers
diagonals (Figure 2b). The rocking of a masonry pier Figure 2: Earthquake response of a hipped roof
can crush the masonry at the corners. Rocking is masonry building – no vertical reinforcement
possible when masonry piers are slender, and when is provided in walls.
weight of the structure above is small. Otherwise, the
piers are more likely to develop diagonal (X-type) Roof
Earthquake-
shear cracking (Figure 2c); this is the most common induced inertia
failure type in masonry buildings. force
In un-reinforced masonry buildings (Figure 3), the Sliding
cross-section area of the masonry wall reduces at the
opening. During strong earthquake shaking, the
building may slide just under the roof, below the lintel
band or at the sill level. Sometimes, the building may
also slide at the plinth level. The exact location of Foundation
sliding depends on numerous factors including
building weight, the earthquake-induced inertia force, Figure 3: Horizontal sliding at sill level in a
the area of openings, and type of doorframes used. masonry building – no vertical reinforcement.
29