Page 12 - EQTips_Eng
P. 12
Learning
6 Earthquake Design
Earthquake Tip and
Construction
How Architectural Features affect Buildings during Earthquakes?
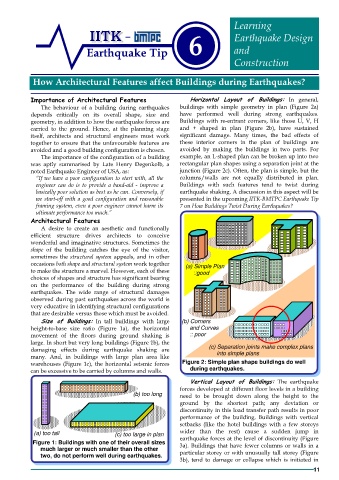
Importance of Architectural Features Horizontal Layout of Buildings: In general,
The behaviour of a building during earthquakes buildings with simple geometry in plan (Figure 2a)
depends critically on its overall shape, size and have performed well during strong earthquakes.
geometry, in addition to how the earthquake forces are Buildings with re-entrant corners, like those U, V, H
carried to the ground. Hence, at the planning stage and + shaped in plan (Figure 2b), have sustained
itself, architects and structural engineers must work significant damage. Many times, the bad effects of
together to ensure that the unfavourable features are these interior corners in the plan of buildings are
avoided and a good building configuration is chosen. avoided by making the buildings in two parts. For
The importance of the configuration of a building example, an L-shaped plan can be broken up into two
was aptly summarised by Late Henry Degenkolb, a rectangular plan shapes using a separation joint at the
noted Earthquake Engineer of USA, as: junction (Figure 2c). Often, the plan is simple, but the
“If we have a poor configuration to start with, all the columns/walls are not equally distributed in plan.
engineer can do is to provide a band-aid - improve a Buildings with such features tend to twist during
basically poor solution as best as he can. Conversely, if earthquake shaking. A discussion in this aspect will be
we start-off with a good configuration and reasonable presented in the upcoming IITK-BMTPC Earthquake Tip
framing system, even a poor engineer cannot harm its 7 on How Buildings Twist During Earthquakes?
ultimate performance too much.”
Architectural Features
A desire to create an aesthetic and functionally
efficient structure drives architects to conceive
wonderful and imaginative structures. Sometimes the
shape of the building catches the eye of the visitor,
sometimes the structural system appeals, and in other
occasions both shape and structural system work together (a) Simple Plan
to make the structure a marvel. However, each of these ::good
choices of shapes and structure has significant bearing
on the performance of the building during strong
earthquakes. The wide range of structural damages
observed during past earthquakes across the world is
very educative in identifying structural configurations
that are desirable versus those which must be avoided.
Size of Buildings: In tall buildings with large (b) Corners
height-to-base size ratio (Figure 1a), the horizontal and Curves
movement of the floors during ground shaking is :: poor
large. In short but very long buildings (Figure 1b), the
damaging effects during earthquake shaking are (c) Separation joints make complex plans
into simple plans
many. And, in buildings with large plan area like
warehouses (Figure 1c), the horizontal seismic forces Figure 2: Simple plan shape buildings do well
can be excessive to be carried by columns and walls. during earthquakes.
Vertical Layout of Buildings: The earthquake
forces developed at different floor levels in a building
(b) too long need to be brought down along the height to the
ground by the shortest path; any deviation or
discontinuity in this load transfer path results in poor
performance of the building. Buildings with vertical
setbacks (like the hotel buildings with a few storeys
(a) too tall (c) too large in plan wider than the rest) cause a sudden jump in
Figure 1: Buildings with one of their overall sizes earthquake forces at the level of discontinuity (Figure
3a). Buildings that have fewer columns or walls in a
much larger or much smaller than the other particular storey or with unusually tall storey (Figure
two, do not perform well during earthquakes.
3b), tend to damage or collapse which is initiated in
11