Page 13 - EQTips_Eng
P. 13
IITK-BMTPC Earthquake Tip 6
How Architectural Features affect Buildings during Earthquakes? page 2
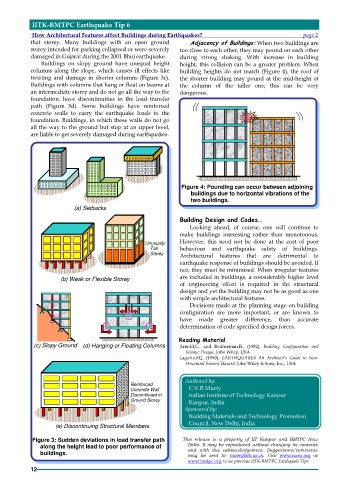
that storey. Many buildings with an open ground Adjacency of Buildings: When two buildings are
storey intended for parking collapsed or were severely too close to each other, they may pound on each other
damaged in Gujarat during the 2001 Bhuj earthquake. during strong shaking. With increase in building
Buildings on slopy ground have unequal height height, this collision can be a greater problem. When
columns along the slope, which causes ill effects like building heights do not match (Figure 4), the roof of
twisting and damage in shorter columns (Figure 3c). the shorter building may pound at the mid-height of
Buildings with columns that hang or float on beams at the column of the taller one; this can be very
an intermediate storey and do not go all the way to the dangerous.
foundation, have discontinuities in the load transfer
path (Figure 3d). Some buildings have reinforced
concrete walls to carry the earthquake loads to the
foundation. Buildings, in which these walls do not go
all the way to the ground but stop at an upper level,
are liable to get severely damaged during earthquakes.
Figure 4: Pounding can occur between adjoining
buildings due to horizontal vibrations of the
two buildings.
(a) Setbacks
Building Design and Codes…
Looking ahead, of course, one will continue to
make buildings interesting rather than monotonous.
Unusually However, this need not be done at the cost of poor
Tall behaviour and earthquake safety of buildings.
Storey Architectural features that are detrimental to
earthquake response of buildings should be avoided. If
not, they must be minimised. When irregular features
(b) Weak or Flexible Storey are included in buildings, a considerably higher level
of engineering effort is required in the structural
design and yet the building may not be as good as one
with simple architectural features.
Decisions made at the planning stage on building
configuration are more important, or are known to
have made greater difference, than accurate
determination of code specified design forces.
Reading Material
(c) Slopy Ground (d) Hanging or Floating Columns Arnold,C., and Reitherman,R., (1982), Building Configuration and
Seismic Design, John Wiley, USA
Lagorio,H,J, (1990), EARTHQUAKES An Architect’s Guide to Non-
Structural Seismic Hazard, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., USA
Authored by:
Reinforced C.V.R.Murty
Concrete Wall
Discontinued in Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
Ground Storey Kanpur, India
Sponsored by:
Building Materials and Technology Promotion
(e) Discontinuing Structural Members Council, New Delhi, India
Figure 3: Sudden deviations in load transfer path This release is a property of IIT Kanpur and BMTPC New
along the height lead to poor performance of Delhi. It may be reproduced without changing its contents
buildings. and with due acknowledgement. Suggestions/comments
may be sent to: nicee@iitk.ac.in. Visit www.nicee.org or
www.bmtpc.org, to see previous IITK-BMTPC Earthquake Tips.
12