Page 27 - Jabalpur_EQ
P. 27
Chapter 2
Selsmologlcal Aspects
nitude earthquakes. This observation can be attributed to the thick alluvium cov
ered valley around Jabalpur city, which absorbed the seismic energy.
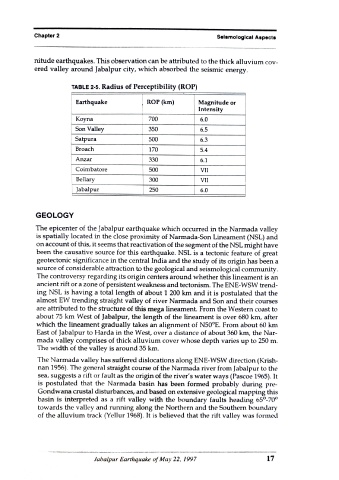
TABLE 2-5. Radius of Perceptibility (ROP)
Earthquake ROP (km) Magnitude or
Intensity
Koyna 700 6.0
Son Valley 350 6.5
Satpura 500 6.3
Broach 170 5.4
Anzar 330 6.1
Coimbatore 500 VII
Bellary 300 VII
Jabalpur 250 6.0
GEOLOGY
The epicenter of the Jabalpur earthquake which occurred in the Narmada valley
is spatially located in the close proximity of Narmada-Son Lineament (NSL) and
on account of this, it seems that reactivation of the segment of the NSL might have
been the causative source for this earthquake. NSL is a tectonic feature of great
geotectonic significance in the central India and the study of its origin has been a
source of considerable attraction to the geological and seismological community.
The controversy regarding its origin centers around whether this lineament is an
ancient rift or a zone of persistent weakness and tectonism. The ENE-WSW trend-
ing NSL is having a total length of about 1 200 km and it is postulated that the
almost EW trending straight valley of river Narmada and Son and their courses
are attributed to the structure of this mega lineament. From the Western coast to
about 75 km West of Jabalpur, the length of the lineament is over 680 km, after
which the lineament gradually takes an alignment of N50°E. From about 60 km
East of Jabalpur to Harda in the West, over a distance of about 360 km, the Nar-
mada valley comprises of thick alluvium cover whose depth varies up to 250 m.
The width of the valley is around 35 km.
The Narmada valley has suffered dislocations along ENE-WSW direction (Krish-
nan 1956). The general straight course of the Narmada river from Jabalpur to the
sea, suggests a rift or fault as the origin of the river's water ways (Pascoe 1965). It
is postulated that the Narmada basin has been formed probably during pre-
Gondwana crustal disturbances, and based on extensive geological mapping this
basin is interpreted as a rift valley with the boundary faults heading 65°-70°
towards the valley and running along the Northern and the Southern boundary
of the alluvium track (Yellur 1968). It is believed that the rift valley was formed
Jabalpur Earthquake of May 22, 1997 17